Hair transplants, which moves hair from one place to another on your head, can be done in several ways. The most common way is grafting. To be a good candidate, you’ll need to have thicker areas of hair on your head. Permanent hair loss can happen due to several reasons, including types of alopecia.
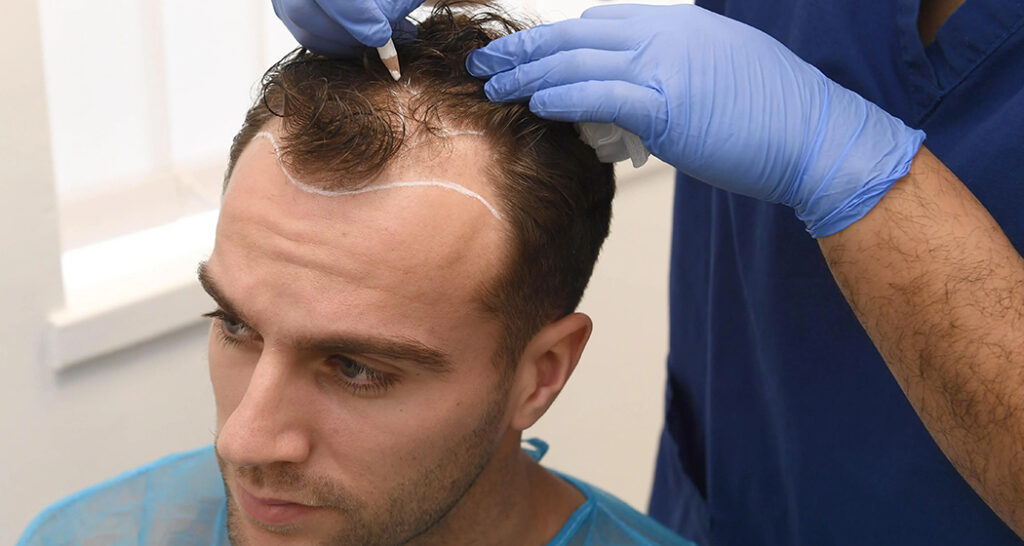
What is a hair transplant?
Hair transplants are a surgery that moves hair to bald or thinning areas of the scalp. Also called hair restoration or hair replacement, it’s usually for people who have already tried other hair loss treatments. Dermatologists (healthcare providers specializing in the skin) or plastic surgeons (healthcare providers specializing in reconstructive procedures) perform hair transplants.
How does a hair transplant work?
The healthcare provider takes grafts, or small pieces of skin, from areas of the body that contain healthy hair. Healthcare providers call this area the donor site. It’s usually on your head, at the back of your scalp where hair tends to be thickest. The healthcare provider moves the grafts to hairless parts of the scalp. Once the transplanted skin heals, it should continue to grow hair.
What conditions does hair restoration surgery treat?
There are many reasons you might lose your hair. Sometimes hair loss is temporary, but it can be permanent. Hair implants may help with permanent hair loss caused by:
- Alopecia areata, an autoimmune disease that attacks hair follicles.
- Androgenic alopecia, or pattern baldness.
- Thyroid diseases or hormonal imbalances.
- Traumatic injuries or burns.
Who is a candidate for hair replacement?
You may be a candidate for hair replacement surgery if you:
- Still have areas of thick hair growth on your scalp.
- Are in good health.
- Have realistic expectations about hair replacement results.
What are the risks of hair transplant surgery?
As with any surgery, a hair transplant comes with risks. These include:
- Allergic reaction to anesthesia.
- Excessive blood loss.
- Failed grafts or flaps.
- Infection.
- Loss of feeling on your scalp.
- Scarring.
What are the side effects of hair transplant surgery?
Side effects of hair transplant surgery are usually temporary. You may experience the following issues on your scalp, at the donor site or where the new hair is:
- Crust or scabs.
- Itching.
- Loss of feeling.
- Pain or throbbing.
- Swelling.
- Tightness.
What are the benefits of hair restoration?
Potential benefits of hair restoration include:
- Fuller head of hair with fewer bald areas.
- Improved self-esteem.
- Permanent hair loss solution.
What is the recovery process after hair transplant surgery?
Most hair transplants are outpatient surgeries, which means you can go home the same day as the procedure. Your recovery process will depend on the type of transplant you have. In the days after surgery, you may be able to:
- Day 1: Remove bandages.
- Day 2: Wash your hair.
- Days 3 to 5: Return to work and start light activities.
- After 10 days: Remove stitches (done by your healthcare provider).
- After 3 weeks: Return to exercise or sports.
How long do the results of a hair transplant last?
It can take up to a year before you see the full results of any hair transplant. The transplanted hair may fall out as the graft or flap heals. This is normal. The hair should grow back. You may need several “touch-up” hair transplant surgeries to achieve a natural-looking result.
When should I see my healthcare provider about a hair transplant?
You’ll likely have several follow-up visits with your healthcare provider after surgery. They will make sure your scalp is healing well. But contact your provider right away if you experience any of the following problems:



