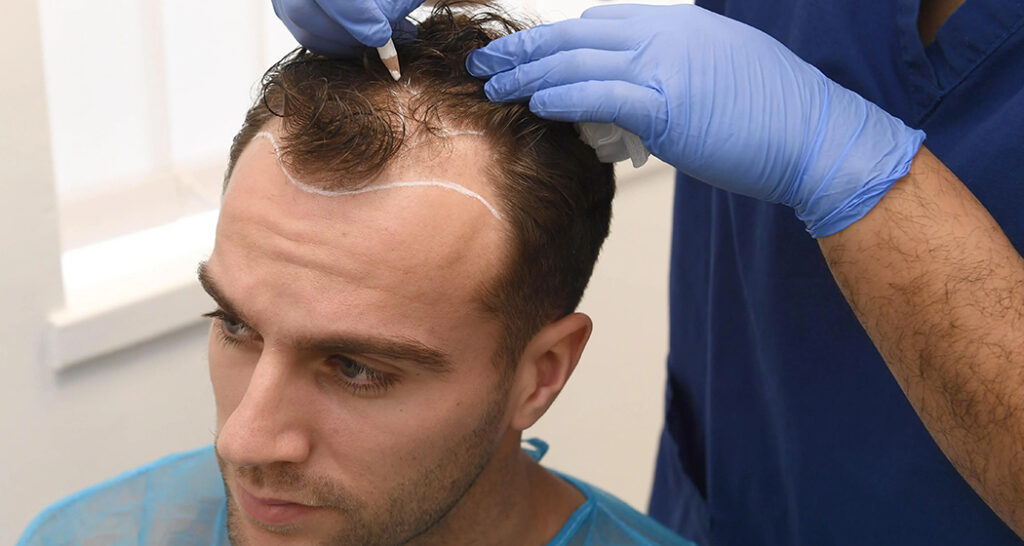
Hair loss affects millions worldwide, with studies showing that approximately 50% of men experience noticeable hair loss by age 50, and nearly 40% of women face similar challenges. While topical treatments and medications can slow hair loss, hair transplantation remains the only permanent solution for restoring natural hair growth. This comprehensive guide examines modern hair transplant techniques, candidacy requirements, procedural details, recovery expectations, and how to select a qualified surgeon.
Understanding Modern Transplant Methods
Contemporary hair transplantation primarily utilizes two advanced techniques:
- Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
- Surgeons remove a strip of hair-bearing scalp from the donor area (typically the back of the head)
- The strip is dissected into individual follicular units under microscopic guidance
- Grafts are then implanted into recipient sites
- Best for: Patients requiring extensive coverage
- Advantages: Higher graft yield in single session
- Considerations: Leaves a linear scar; longer recovery
- Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
- Individual follicular units are extracted directly from the donor area using micro-punches
- No linear scar results from this minimally invasive approach
- Best for: Patients preferring short hairstyles
- Advantages: Virtually undetectable scarring
- Considerations: More time-consuming; higher cost
Ideal Candidate Profile
Successful hair transplant candidates typically exhibit:
- Stable donor area with sufficient hair density
- Realistic expectations about outcomes
- Good overall health without uncontrolled medical conditions
- Patterned hair loss (rather than diffuse thinning)
The Surgical Process
A typical hair transplant procedure follows these steps:
- Consultation & Planning
- Hairline design using facial proportions
- Determination of graft requirements (usually 1,500-3,000 grafts)
- Procedure Day
- Local anesthesia administration
- Graft harvesting (4-8 hours depending on technique)
- Implantation into recipient sites
- Post-Procedure
- Initial recovery (1-2 weeks)
- Temporary “shock loss” of transplanted hairs
- Gradual new growth (3-6 months)
- Final results visible (12-18 months)
Critical Considerations
Success Factors:
- Surgeon skill and experience
- Proper graft handling
- Appropriate post-operative care
Potential Risks:
- Infection (rare with proper protocols)
- Unnatural-looking results (avoidable with skilled surgeons)
- Temporary numbness or swelling
Cost & Selection Criteria
Hair transplant costs vary significantly:
- United States: $4,000-$15,000
- Europe: €2,500-€10,000
- Asia: $1,500-$6,000
When selecting a surgeon:
- Verify board certification (ABHRS preferred)
- Review before/after portfolios
- Inquire about graft survival rates
- Avoid “hair mills” offering unrealistically low prices
Future Innovations
Emerging technologies promise to enhance results:
- Robotic FUE systems for improved precision
- Stem cell therapies to expand donor supply
- Enhanced growth factors to accelerate recovery
Conclusion
Hair transplantation offers a scientifically proven, permanent solution for hair restoration when performed by qualified surgeons. While the procedure requires significant investment and patience during the growth phase, the psychological and aesthetic benefits can be life-changing. Prospective patients should thoroughly research their options, maintain realistic expectations, and commit to proper aftercare for optimal outcomes.
Remember: A successful hair transplant doesn’t stop natural hair loss progression. Many patients benefit from combining surgical restoration with ongoing medical therapy (like finasteride or minoxidil) to preserve existing hair.
Reference Article:A Pill or a Procedure? Decoding Hair Transplants and Hair Loss Medication